Hydroelectric power is the oldest and the “greenest” source of renewable energy. In Germany, the potential would appear to be completely exploited, while large-scale projects in developing countries are eliciting strong criticism due to their major impact on the environment. Researchers at Technische Universitaet Muenchen (TUM) have developed a small-scale hydroelectric power plant that solves a number of problems at the same time: The construction is so simple, and thereby cost-efficient, that the power generation system is capable of operating profitably in connection with even modest dam heights. Moreover, the system is concealed in a shaft, minimizing the impact on the landscape and waterways. There are thousands of locations in Europe where such power plants would be viable, in addition to regions throughout the world where hydroelectric power remains an untapped resource.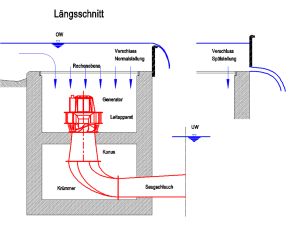
Smaller power stations entail considerable financial input and are also not without negative environmental impact. Until now, the use of hydroelectric power in connection with a relatively low dam height meant that part of the water had to be guided past the dam by way of a so-called bay-type power plant — a design with inherent disadvantages.
A solution to all of these problems has now been demonstrated, in the small-scale hydroelectric power plant developed as a model by a team headed by Prof. Peter Rutschmann and Dipl.-Ing. Albert Sepp at the Oskar von Miller-Institut, the TUM research institution for hydraulic and water resources engineering. Their approach incurs very little impact on the landscape. Only a small transformer station is visible on the banks of the river. In place of a large power station building on the riverside, a shaft dug into the riverbed in front of the dam conceals most of the power generation system. The water flows into a box-shaped construction, drives the turbine, and is guided back into the river underneath the dam. This solution has become practical due to the fact that several manufacturers have developed generators that are capable of underwater operation — thereby dispensing with the need for a riverbank power house.
